NSX-T Data Center leverages BGP EVPN technology to interconnect and extend NSX-managed overlay networks to other data center environments not managed by NSX, VXLAN encapsulation is used between NSX TEPs (edge nodes and hypervisors) and external network devices to ensure data plane compatibility.
Two connectivity modes are supported for EVPN implementation in NSX-T Data Center:
| Inline Mode: |
|---|
In this mode, the tier-0 gateway establishes MP-BGP EVPN control plane sessions with external routers to exchange routing information. In the data plane, edge nodes forwards all the traffic exiting the local data center to the data center gateways and incoming traffic from the remote data center to the hypervisors in the local data center. Since the edge nodes are in the data forwarding path, this model is called the Inline model. 
|
| Route Server Mode: |
|---|
In this mode, the tier-0 gateway establishes MP-BGP EVPN control plane to exchange routing information with the external router or route reflectors. In the data plane, ESXi hypervisors forward the traffic to external networks either to the data center gateways or remote ToR switches over VXLAN tunnels. TEPs used for the data plane VXLAN encapsulation are the same than the ones used for GENEVE encapsulation. 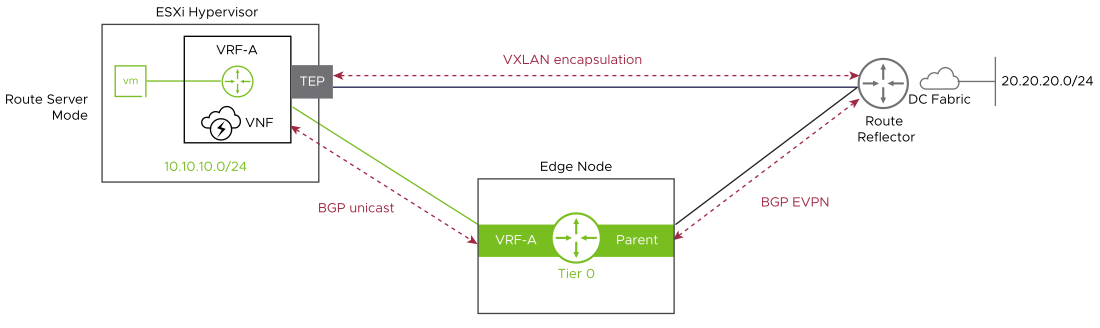
|
Route Distinguishers and Route Targets in NSX-T Data Center:
With NSX-T Data Center BGP implementation, route distinguishers (RD) can be either set automatically or manually. The following table details the supported RD modes in the Inline and Route Server modes.| Mode | Auto RD | Manual RD |
|---|
Inline | Supported. Only type-1 is supported. You must configure the RD Admin field. The RD Admin field must be in the format of an IP address. The RD admin field is used to fill the Administrator subfield in the RD. The 2-byte Assigned Number subfield will be allocated a random number in the range for each RD generation. Generated auto RD is checked against other manually configured RDs to avoid any duplicates.
| Supported. Both type-0 and type-1 are allowed, but type-1 is recommended. No RD Admin field is required to be configured. Configure manual RD is checked against other auto RDs to avoid any duplicates.
|
Route Server | | Supported. Both type-0 and type-1 are allowed, but type-1 is recommended. No RD Admin field is required to be configured. Configured manual RD is checked against other auto RDs to avoid any duplicates.
|
Limitations and Caveats:
NSX supports L3 EVPN by advertising and receiving IP prefixes as EVPN Route Type-5. NSX-T generates a unique route MAC for every NSX Edge VTEP in the EVPN domain. However, there may be other nodes in the network that are not managed by NSX-T, for example, physical routers. You must make sure that the router MACs are unique across all the VTEPs in the EVPN domain. The EVPN feature supports NSX Edge nodes to be either the ingress or the egress of the EVPN virtual tunnel endpoint. If an NSX Edge node receives EVPN Route Type-5 prefixes from its eBGP peer that needs to be redistributed to another eBGP peer, the routes are re-advertised without any change to the next hop. In multi-path network topologies, it is recommended that ECMP is enabled for the NSX BGP EVPN control plane, so that all the possible paths can be advertised by the tier-0 gateway. This will avoid any potential traffic blackhole due to asymmetric data path forwarding. A tier-0 gateway can span across multiple edge nodes. However, specifying a unique route distinguisher for each edge node or TEP (either via auto or manual configuration) is not supported. As a result, the use of ECMP on the peer router is not supported. Route maps are not supported for EVPN address family. Recursive route resolution for gateway IP via default static route is not supported.
|
Limitations and caveats for Inline mode: Only BGP Graceful Restart in Helper Mode is supported. Only eBGP is supported between tier-0 SRs and external routers. Only one TEP is supported per edge node. The use of loopback interfaces for TEP is highly recommended.
|
Limitations and caveats for Route Server mode: The High Availability mode on the tier-0 must be set to active-active. The manual Route Distinguisher and manual Route Targets are supported. BGP Graceful Restart, Helper Mode, and Restarted Mode are not supported. Only eBGP is supported between hosted VNFs and tier-0 VRF gateways. eBGP multihop using loopbacks is required between tier-0 SRs and external routers. Using uplinks for eBGP neighbor session is not supported for EVPN Router Server mode operation. The VNF uplink towards the tier-0 SR VRF must be in the same subnet as the Integrated Routing and Bridging (IRB) on the data center gateways.
|



Comments
Post a Comment