NSX-T Data Center leverages BGP EVPN technology to interconnect and extend NSX-managed overlay networks to other data center environments not managed by NSX, VXLAN encapsulation is used between NSX TEPs (edge nodes and hypervisors) and external network devices to ensure data plane compatibility.
Two connectivity modes are supported for EVPN implementation in NSX-T Data Center:
| Inline Mode: |
|---|
In this mode, the tier-0 gateway establishes MP-BGP EVPN control plane sessions with external routers to exchange routing information. In the data plane, edge nodes forwards all the traffic exiting the local data center to the data center gateways and incoming traffic from the remote data center to the hypervisors in the local data center. Since the edge nodes are in the data forwarding path, this model is called the Inline model. |
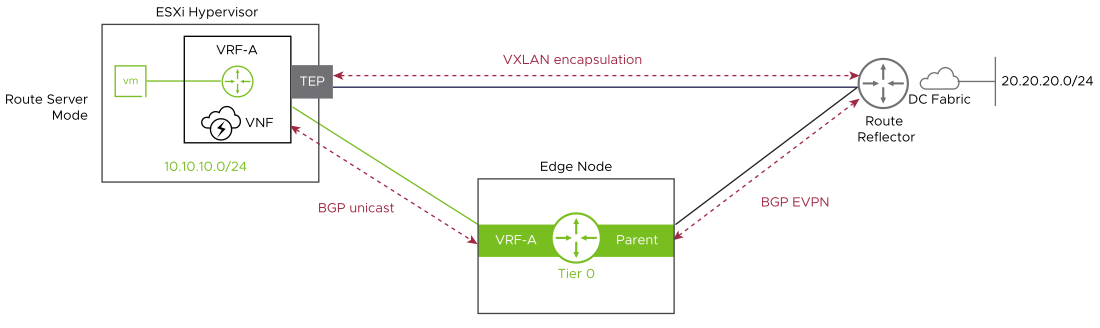
| Route Server Mode: |
|---|
In this mode, the tier-0 gateway establishes MP-BGP EVPN control plane to exchange routing information with the external router or route reflectors. In the data plane, ESXi hypervisors forward the traffic to external networks either to the data center gateways or remote ToR switches over VXLAN tunnels. TEPs used for the data plane VXLAN encapsulation are the same than the ones used for GENEVE encapsulation. |
Route Distinguishers and Route Targets in NSX-T Data Center:
| Mode | Auto RD | Manual RD |
|---|---|---|
Inline |
|
|
Route Server |
|
|
Limitations and Caveats:
|
Limitations and caveats for Inline mode:
|
Limitations and caveats for Route Server mode:
|